Online Dental Trauma Guide: Part I Fracture Injuries
Enamel fractures
Enamel fractures
An enamel fracture is loss of enamel with no visible sign of dentine exposure.
Clinical findings
A tooth with an enamel fracture is:
Usually asymptomatic.
Not tender to touch.
Not mobile.
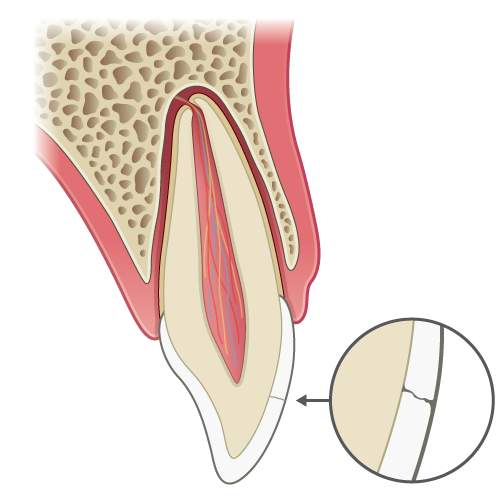
llustration: Longitudinal section of a tooth showing an enamel fracture.

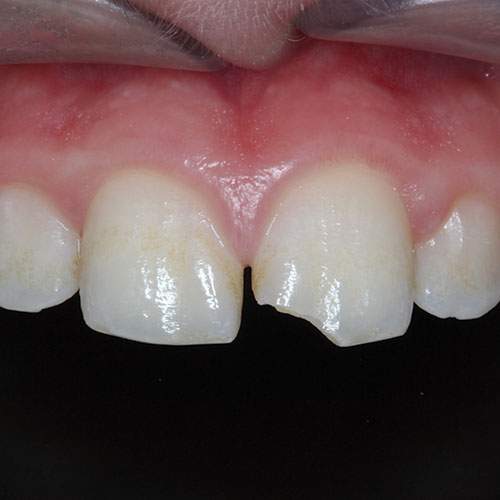
Clinical image: Enamel fracture of the UL1.
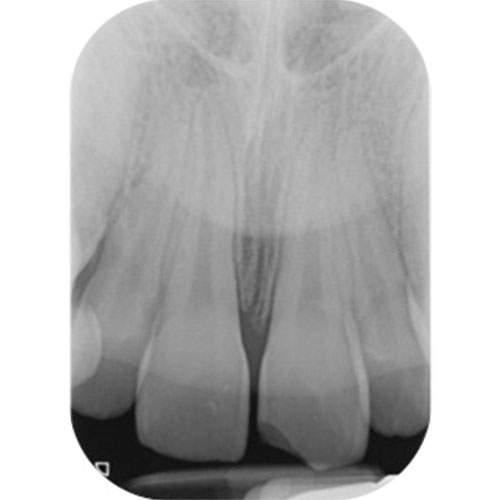
Radiograph: Periapical radiograph of the UL1 showing normal periodontal ligament outline.
Radiographic findings
A radiograph of a tooth with an isolated enamel fracture will appear normal
If a combined luxation/ displacement injury or root fracture is suspected, an upper standard occlusal can be helpful to aid diagnosis.
If the fragment has not been accounted for and a soft tissue laceration is present, it would be prudent to obtain soft tissue views.
Radiographic Tip
If fractured pieces are not found look for evidence of soft tissue laceration and consider the possibility that the missing fragments may be embedded within the soft tissues.
A radiograph taken at 30-50% of the normal exposure will demonstrate radio-opaque masses, if present (see image below for patient positioning technique).
Removal of the fragment is essential to prevent scarring
If found it may be appropriate to refer the patient to an oral surgeon for management.

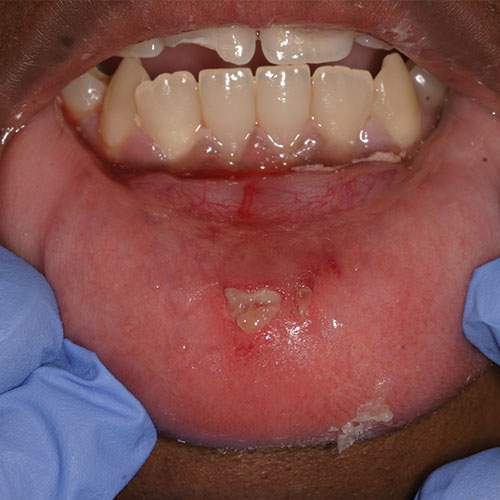
Clinical image: Lower lip laceration in a patient with crown fracture of the UR1.
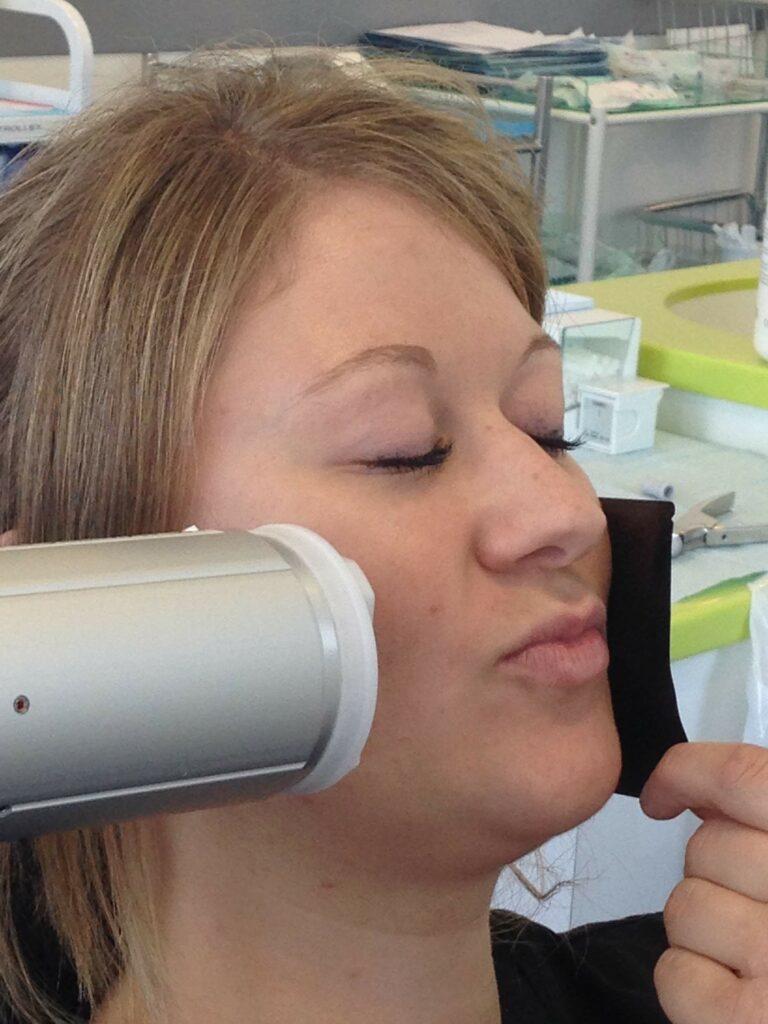
Radiographic technique: Showing the patient positioning to look for fragments in the soft tissues of the lip.
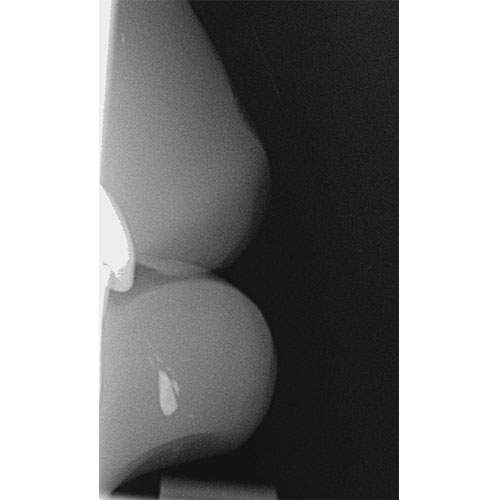

Radiograph: Showing the presence of a radio-opaque mass in the lower lip.
Management of primary teeth
In primary teeth it is usually sufficient to smooth sharp edges to prevent trauma to the lip and tongue.
Management of permanent teeth
If the tooth fragment is available and can be relocated with ease then an attempt could be made to bond it to the tooth
If the fragment cannot be repositioned with ease (because it is too small or has been lost) then the tooth can be restored with composite resin
If the fracture is minor the tooth could simply be smoothed down.
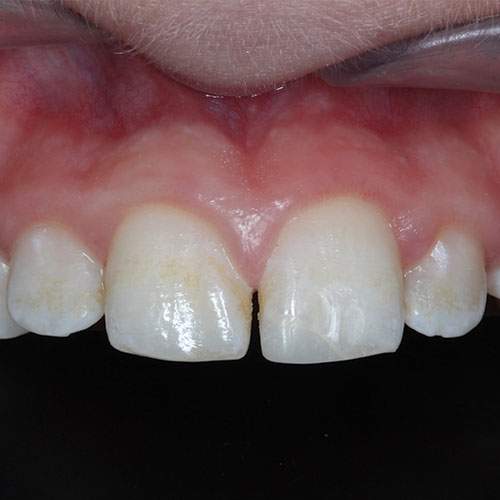
Clinical Case 1: Repaired enamel fracture of the UL1
UL1 enamel fracture restored with composite resin.
Note: This technique is described in detail in the topic on enamel-dentine fractures.
Monitoring: A one year follow-up period is advised as part of routine care.




